The main challenge of our time involves extracting meaningful value from data while managing and storing it. The structured systems of databases help solve this problem by organizing and retrieving information, but testing them becomes more complicated as they grow.
To resolve these problems, you can consider database testing tools, which can be your solution. In this article, we’ll break down what database testing is, the key types of testing, when and why the best database testing tools are needed, and how to choose the right one for your needs.
What is database testing?
To put it simply, database or DB testing is applied to be sure that databases function correctly and efficiently together with their connected applications. The mentioned process verifies the system’s data storage capabilities and retrieval functions and data processing efficiency while keeping consistency during all operations.
👀 Let’s consider an example: The software testing process for new user sign-ups starts with database verification of correct information entry. The testers would run a specific SQL query to confirm that the users table received the new record and that the password encryption worked correctly.
Checking that their user ID correctly links to newly generated user profile records can be done by executing a join query to verify data consistency between the user_profiles and users tables.
The testers would also attempt to create a new account with an existing email address to validate database integrity; they would follow business rules for unique data to verify that the database correctly rejects the request and prevents a copy of the record.
Types of Databases: What are They?
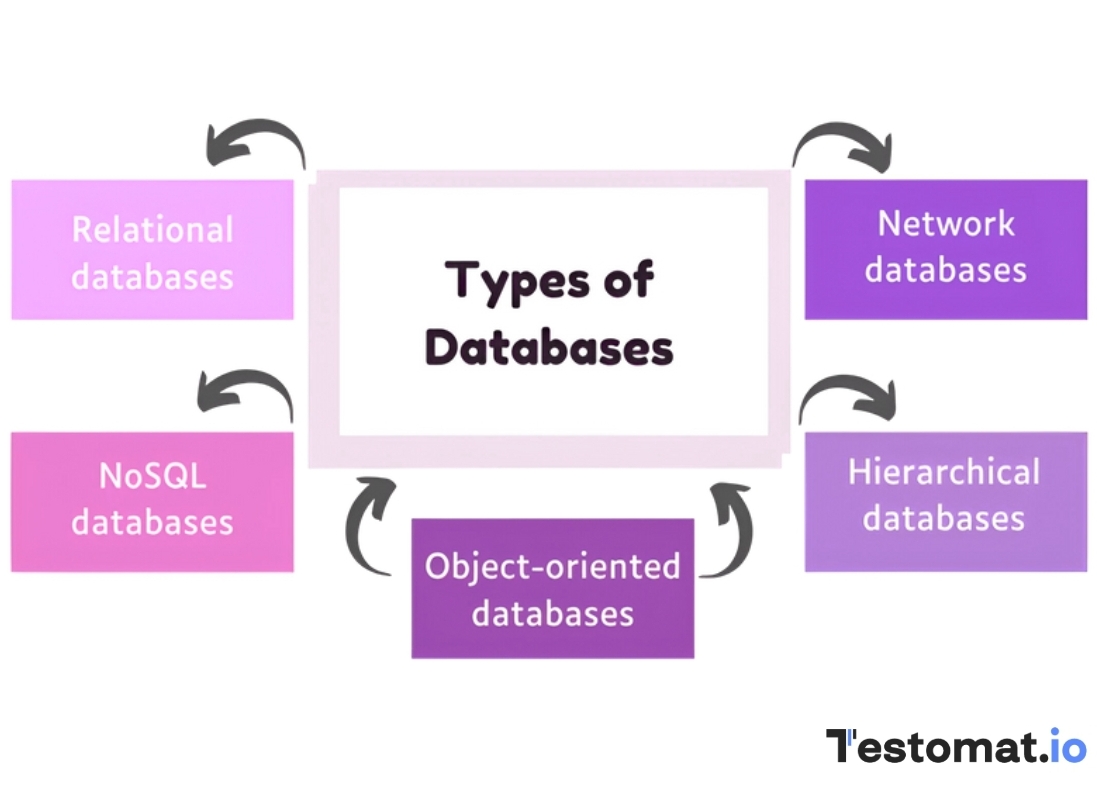
The existence of multiple types of databases stems from the fact that no Information system can fulfill all requirements for every web application. Each database system has its own purpose to manage particular data types while addressing specific business requirements. The different database types exist because they meet specific company needs, which include data structure management and large-scale system requirements, performance, and consistency standards.
- Relational Databases or SQL Databases. They are known as the most common type, in which tables are used to organize data for easy data management and retrieval. Each table consists of rows and columns, where rows are records, and columns represent different attributes of that data.
- NoSQL Databases. They are designed to work with large and unstructured data sets and do not rely on tables. These databases are a good option for big data applications such as social media and real-time analytics because they support flexible data management of documents and graphs.
- Object-Oriented Databases. They store data as objects which follows object-oriented programming principles to eliminate the need for a separate mapping layer, thus simplifying development.
- Hierarchical Databases. This type arranges data in a tree-like structure, where each record has a parent-child relationship with other records, and forms a hierarchy. Thanks to this structure, it is easy to understand the relationships between data and access. These databases are used in applications that require strict data relationships.
- Cloud Databases. These databases keep information on remote servers, which can be accessed via the internet. This type provides scalability, where you can adjust resources based on your needs. Because they can be either relational or NoSQL, cloud databases are a flexible solution for businesses with global teams or remote users who need universal access to data.
- Network Databases. Based on a traditional hierarchical database, these databases provide more complex relationships, where each record can have multiple parent and child records, and form a more flexible structure. This type is suitable if there is a need to represent interconnected data with many-to-many relationships.
When And Why Should We Conduct Database Testing?
A fully functional database is essential for the adequate performance of software applications. It is utilized to store and create data corresponding to its features and respond to the queries.
However, if the data integrity is impacted, it can cause a negative financial impact on the organization. This is because data integrity leads to errors in decision-making, operational inefficiencies, regulatory violations, and security breaches.
Thus, performing database testing to handle and manage records in the databases effectively is a must for everyone – from the developer who is writing a query to the executive who is making a decision based on data. Before investing in a software solution, let’s review why you need to conduct quality assurance for your databases:
#1: Pre-Development
Making sure the database is built correctly and meets the project’s goals is critical to avoiding problems later. Testers need to check the schema design to be sure tables are set up properly, and they should check normalization to avoid storing the same information in multiple places.
Also, quality assurance specialists shouldn’t forget to verify constraints and indexing to implement data rules and guarantee good performance later.
#2: Before Going Live
The system requires complete verification for datasets to occur immediately before its launch to guarantee perfect functionality between the database and application, which results in a reliable first-day experience for users. The test process should validate fundamental operations (create, read, update, delete) in databases and verify stored procedures and triggers for errors.
#3: Migration of Data
The process of verifying datasets quality during migration guarantees that the information flows correctly and without error. The main goal at this point is to verify that migration does not create errors, which include missing records, corrupted values, or mismatched fields, and maintains the same information as the old one.
#4: Updates and Changes
If there have been patching, upgrading, and structural changes in the database, it creates potential risks for existing system functionality. So, it is mandatory to verify that new modifications do not interfere with current operational processes or generate unforeseen system errors.
The main priority should be to perform regression tests on queries and triggers and views, and dependent web applications. The re-validation process enables testers to verify that both existing and new features operate correctly, which maintains system stability throughout each update cycle.
#5: Security and Compliance
You need to give immediate attention to security measures and compliance standards in order to protect sensitive data, which is kept in databases. You need to stop illegal access and data breaches, make sure that it adheres to important regulations (for example, GDPR and HIPAA). Verification of permissions, encryption, and testing for SQL injection attacks are necessary to protect the datastore from hackers, build customer trust, and prevent your company from legal and financial risks.
#6: Data Consistency and Integrity
The verification of database stability requires ongoing checks to guarantee data accuracy and consistency, even when your datastore appears stable. Your business will face major problems when small errors, such as duplicated entries or broken data links, occur.
Types of Database Testing
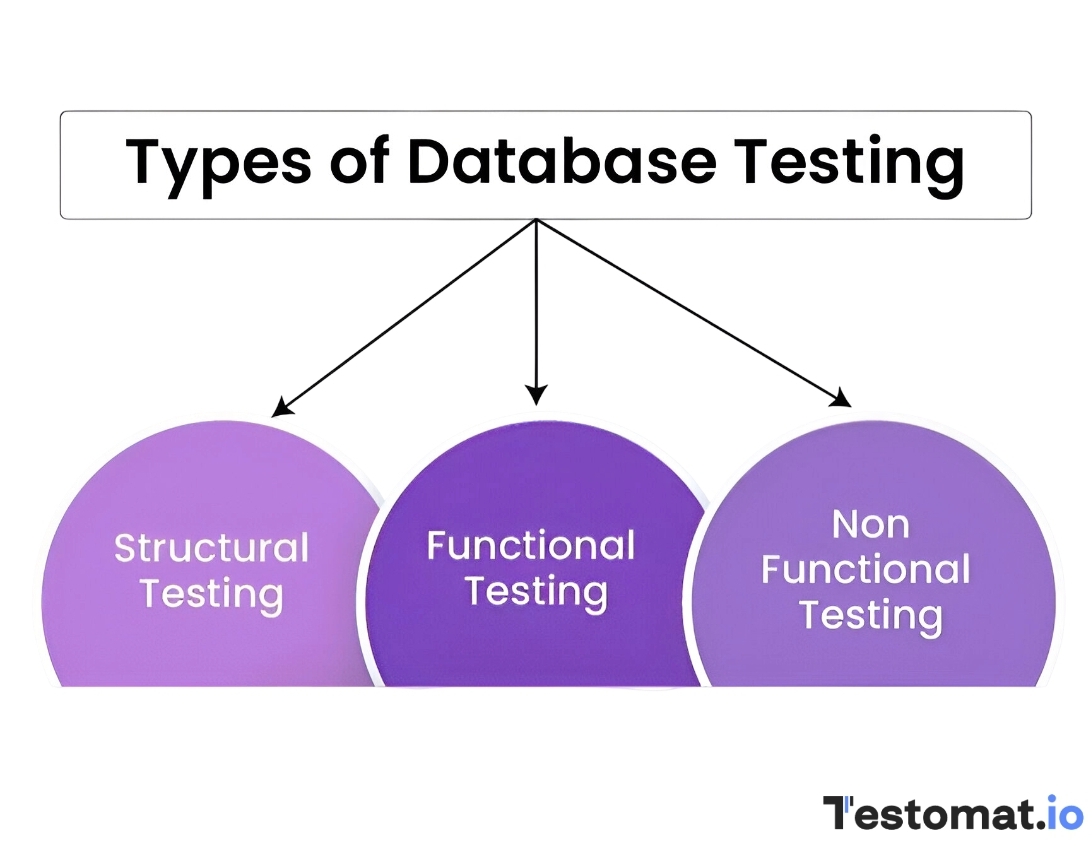
Structural
This type aims to verify that the database’s internal architecture is correct. It helps to validate the operational functionality of database systems and check all the hidden components and elements, which are not visible to users (tables and schemas).
Functional
The purpose of functional testing is to verify how a database operates on user-initiated actions, including form saving and transaction submission.
- White box. It helps analyze the database’s internal structure and test database triggers and logical views to ensure their inner workings are sound.
- Black box. It helps test the external functionality, such as data mapping and verifying stored and retrieved data.
Non-Functional
- Data Integrity Testing. Thanks to this type of testing, you can verify that information remains both accurate and uniform throughout the database. Also, you can check loss and duplication of datasets to keep information as reliable and trustworthy as possible.
- Performance Testing. The evaluation of the performance of databases takes place under different operational conditions and evaluates the database’s response time, throughput, or resource utilization through load testing and stress testing.
- Load Testing. This type aims to accurately assess how the database will perform under real-life usage. It can be done by checking a database’s speed and responsiveness and simulating realistic user traffic.
- Stress Testing. This extreme form of load testing pushes a database to its breaking point. It evaluates the database’s performance by hitting it with an unusually large number of users or transactions over an extended period. The test helps identify boundaries while showing performance problems that happen when the system is under high stress.
- Security Testing. This type is applied to identify database vulnerabilities while confirming protection against unauthorized access and information leaks. The system requires verification of role-based access controls to be sure that users with particular roles can only access and perform authorized actions, which protects the entire system.
- Data Migration Testing. It is used to reveal problems that occur when information moves between different system components to ensure its integrity, accuracy, and completeness.
When to Use Database Testing Tools?
Let’s explore when you can use database testing tools:
| System Upgrades or Patches | If you need to verify that the database and application functionality stay correct after system updates and patches, which have been implemented. If you need to check that new software versions have not introduced any bugs or compatibility issues which could impact the system. |
| Deployment Readiness | If you need to check that the database is fully prepared for a new application to go live in a production environment. If you need to guarantee that all configurations and connections in datasets are properly established to prevent any operational failures on the first day of the launch. |
| Backup & Recovery Validation | If you need to make sure that backup operations function properly and your datasets can be fully restored in case of system failure or data loss. |
| Data Integrity Validation | If your database grows in size and complexity, and it becomes difficult to manually check all the rules and millions of records for detecting errors – duplicate data, and broken relationships. |
| Security & Vulnerability | If you need to provide database security flaw detection and automatic verification of access controls and permissions for every user role, which cannot be achieved through manual processes. |
| Automated deployment Process | If you need to immediately test every build by integrating database testing tools with CI/CD pipelines. |
What Are The Types Of Database Testing Tools For QA?
Let’s overview the types of tools used for database testing.
General Database Testing & Database Automation Testing Tools
These tools enable automated functional testing of databases to verify schemas and stored procedures, and triggers, and data integrity and CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete). They ensure repeatable, consistent tests, especially after frequent updates or deployments, and are used for:
- Unit testing SQL queries or stored procedures.
- The process of validating database logic matches the business rules that need to be followed.
- Regression testing after schema changes.
Database Performance Testing Tools & Database Load Testing Tools
These tools enable the simulation of real-world loads and traffic on a database to test its performance under stress conditions and concurrent user loads and large datasets. They are applied for:
- Stress testing queries under thousands of concurrent users.
- Checking query response times under peak load.
- Capacity planning before scaling infrastructure.
Database Migration Testing Tools
The tools ensure information movement between systems while checking record counts and data mappings, and referential integrity. They help to prevent data loss, corruption, and compliance issues. You can choose them if you need to:
- Verify migration of the records during cloud adoption.
- Check schema compatibility after upgrades.
- Guarantee the integrity of records after migration.
SQL Injection & Security Testing Tools
These tools allow you to focus on database security while detecting SQL injection vulnerabilities and weak permissions, and unencrypted data. They are helpful in the following cases:
- Identifying SQL injection risks in queries.
- Checking access controls, roles, and permissions.
- Validating encryption and security compliance.
Overview Of The Best Database Testing Tools
SQL Test (for SQL Server databases)
It is an easy-to-use database unit testing tool to generate a real-world workload for testing, which can be used on-premises as well as in the cloud. The tool integrates with major databases to offer a complete unit test framework which supports different database testing requirements. The learning curve for this tool is easy for SQL developers who already know SSMS.
- Key Features: Integrates with SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), allows unit testing of T-SQL stored procedures, functions, and triggers.
- Common Use Cases: Ad-hoc data checks, data integrity audits, regression testing, and post-migration data validation.
- Best for: Developers and QA engineers who need quick, flexible, and precise control over their data checks without relying on a third-party tool.
- ✅ Pros: The system provides flexibility and does not require external tools while allowing direct control.
- 🚫 Cons: SQL Server–only, limited scope beyond unit tests.
NoSQLUnit (NoSQL-specific Testing)
Used as a framework for validation of NoSQL databases to make sure that a database is in a consistent state before and after a test runs. The learning curve for this tool is medium because it needs Java/JUnit programming skills.
- Key Features: JUnit extension for NoSQL databases (MongoDB, Cassandra, HBase, Redis, etc.), data loading from external sources.
- Common Use Cases: Unit and integration testing for applications built on NoSQL databases.
- Best for: Java teams working with diverse NoSQL technologies.
- ✅ Pros: The tool provides support for multiple NoSQL databases and includes automated features for test data setup and teardown.
- 🚫 Cons: Java dependency, not beginner-friendly for non-Java developers.
DbUnit (Java-based)
It is a Java-based extension for JUnit that’s used for database-driven verification, aiming to put the database in a known state between each test run. It helps to make sure that the tests are repeatable and that results aren’t affected by a previous test’s actions. The learning curve for this tool is moderate because it needs knowledge of JUnit and XML.
- Key Features: JUnit extension for relational DB testing, XML-based datasets, integration with continuous integration (CI) pipelines.
- Common Use Cases: Unit and integration testing for Java applications, especially for ensuring that business logic correctly interacts with the database.
- Best for: Java applications with relational databases.
- ✅ Pros: Well-established, CI/CD friendly, good for regression.
- 🚫 Cons: The system has the following disadvantages: Verbose XML datasets, less intuitive for beginners, and Java-only.
DTM Data Generator
It is a user-friendly test data generator for creating large volumes of realistic test data, which helps testers fill a database with a huge amount of information for performance and load tests. The learning curve for this tool is easy to moderate and requires setup for complex rules.
- Key Features: Generates synthetic test data, customizable rules, and supports multiple databases.
- Common Use Cases: Populating databases with large datasets for running tests.
- Best for: Teams needing bulk test data quickly.
- ✅ Pros: Fast data creation, supports constraints and relationships.
- 🚫 Cons: Paid license for full features, not suitable for dynamic/continuous test data generation.
Mockup Data
The data generation tool creates a genuine datastore and application test data, which improves data quality and accuracy while identifying data integration and migration problems. The learning curve for this tool is easy.
- Key Features: Random data generator with templates, custom rules, and quick CSV/SQL export.
- Common Use Cases: Creating sample data for demos, prototypes, and quality assurance (QA) environments.
- Best for: Developers/testers who need small to medium-sized datasets.
- ✅ Pros: Quick setup, customizable data, export flexibility.
- 🚫 Cons: The system has limited scalability for very large datasets and is less suited for complex relational logic.
DataFaker
It is a Java and Kotlin library designed to streamline test data generation to populate databases, forms, and applications with a wide variety of believable information—such as names, addresses, phone numbers, and emails, without using real, sensitive information.
- Key Features: Open-source library for generating fake data (names, addresses, numbers, etc.), supports Java/Python. The learning curve for this tool is moderate and requires programming to configure.
- Common Use Cases: Generating realistic test data for applications and database validation.
- Best for: Developers comfortable with code-based test data creation.
- ✅ Pros: Open-source nature, flexibility, high customizability, and realistic datasets.
- 🚫 Cons: The system requires coding skills and does not have a graphical user interface, and may need additional work for relational data.
Apache JMeter
The most popular performance testing tools, which can also be used for performance DB testing, simulate multiple users accessing the system, executing SQL queries, and monitoring response time. The learning curve for this tool is moderate, but complex for advanced scenarios.
- Key Features: Open-source load testing tool, supports JDBC connections, simulates heavy user loads on databases.
- Common Use Cases: Performance and stress testing databases, analyzing query response times.
- Best for: QA teams needing performance validation at scale.
- ✅ Pros: The platform offers free access and flexibility, b community backing and supports multiple information systems.
- 🚫 Cons: The system requires advanced technical knowledge to establish, and it operates with more complexity than basic data generators.
How to Choose the Right Tool For Database Testing
To choose the right tool for the QA process, you must first define your goals. Your purpose for testing will determine which tools you need to use. Whether you need to validate schemas, queries, and stored procedures, test a database’s performance under heavy load, data migrations, integrity, or vulnerabilities, you should know it from the start.
✅ Know Your Database Type and Match Tool to It
The database type determines the quality assurance strategy and test plan because relational and NoSQL databases require different QA techniques. So you should select a tool, which is designed to work with a specific structure of the datastore to ensure accurate and effective QA.
✅ Choose A Tool That Matches The Skills Of Your Teams
A database testing tool is only as effective as the team using it, so you must choose one that matches their existing skill set. A complex tool (from the best database testing tools list) chosen for a team that uses graphical interfaces will create a long learning process, which will delay the project’s completion.
✅ Assess The Automated Features And The Ability To Connect With Other Systems
The integration of database testing tools with your current workflow and automated QA capabilities stands as a vital requirement for modern, efficient software development processes. So, you should opt for database testing tools which integrate well with your CI/CD pipeline to run tests automatically with each code modification.
✅ Find The Balance Between Cost And Functionality
The selection process requires a vital evaluation of tool expenses relative to their available features. The fundamental needs of free open-source tools are met, but paid solutions provide both advanced features and professional assistance, and superior performance.
Undoubtedly, your final choice should be based on the strengths of the product from the database testing tools list and how they meet your project’s specific needs. However, it is important to note that you need to carry out a pilot test on a small project (or use the free trial) before proceeding with a complete commitment.
The assessment should evaluate how simple the system is to deploy, how much area it covers, and how well your team accepts it. Only if the pilot is successful should you use the tool for a larger project.
The Role of AI in Modern Database Test Automation Tools
AI transforms DB testing through automated systems, which decreases the need for human manual work. The system generates test cases to check complex databases and produces authentic test data with multiple characteristics while maintaining data confidentiality. The streamlined method enables faster and smarter database verification, which results in higher reliability at a reduced cost. To sum up, AI in DB testing offers:
- Optimizing settings of the datastore for peak performance.
- Finding and fixing data inconsistencies automatically.
- Using data analysis to help design database schema elements, which results in optimal structural designs.
- Predicting upcoming problems that could lead to storage bottlenecks and query slowdowns, and hardware failures.
- Interacting with databases through natural language interfaces.
Bottom Line: Ready To Boost Your Database Quality with Database Testing Tools?
Database testing automation tools are essential for ensuring that your databases are working correctly and reliably. These database testing tools are crucial for automating tasks that would be difficult to do manually. Choosing the optimal tool among a variety of database testing tools depends on several factors, including:
- The type of database you’re using.
- Your project’s specific requirements.
- The kinds of tests you need to perform.
- The core functionality and features you are looking for.
- Affordable price for the tools, which suit your needs and budget.
Furthermore, the integration of AI into DB testing automates routine tasks, enhances dataset quality, removes inconsistencies, and provides advanced analytics. So the correct selection guarantees that you will get the appropriate functionality needed to perform effective quality assurance. Contact Testomat.io today to learn how our services can help you prepare a good test environment and resolve performance issues with database testing tools.
Frequently asked questions
What are the key features of Testomat.io for database testing?

Testomat.io streamlines database testing with AI-powered test orchestration, allowing you to design, execute, and maintain automated test cases effortlessly. It integrates with popular database systems, providing real-time feedback on test performance and results. With intuitive test creation and detailed reporting, Testomat.io simplifies the process while ensuring high accuracy and efficiency.
What are the advantages of using Testomat.io for database testing?

Testomat.io offers several key advantages: faster test creation, smarter execution with prioritization, and automatic test result analysis. Its user-friendly interface and integration with popular databases allow teams to quickly identify and fix issues. Plus, with its cloud-based platform, you can collaborate in real time and scale tests as your project evolves.